301-Redirects & SEO: The Hidden Costs of "Quick Fixes"
Despite everything you've heard about redirecting for SEO, it is almost never an idea fix...
301 redirects have been actively used by developers and SEO consultants when rebranding a site or changing its structure to avoid usability issues and save link equity.
Join us to discuss this topic (Wednesday, 1 pm est, aslo available as a free replay!)
While in many cases, 301 redirects are unavoidable, there are a few important things you need to know about them, in terms of SEO:
301-Redirect Leak Link Equity
In the past, Google said a small amount of PageRank is lost through a 301 redirect.
In 2016, Moz published a case study sharing exactly how much is lost. Permanent redirects cause a 15% drop in organic traffic. If you use chain redirects (where one page redirects to another redirect which finally leads to a live page), 15% of organic traffic is lost with each redirect.
In the experiment, the site used redirects from /barstool.html to /bar-tool.html to /29-inch-bar-stool.html, and the consistent loss of organic traffic looked like this:
Moreover, there was no evidence of recovery (redirected pages recovering lost visibility) after months of the redirects being set up.
These findings were also in accordance with the original PageRank paper (published in 1998).
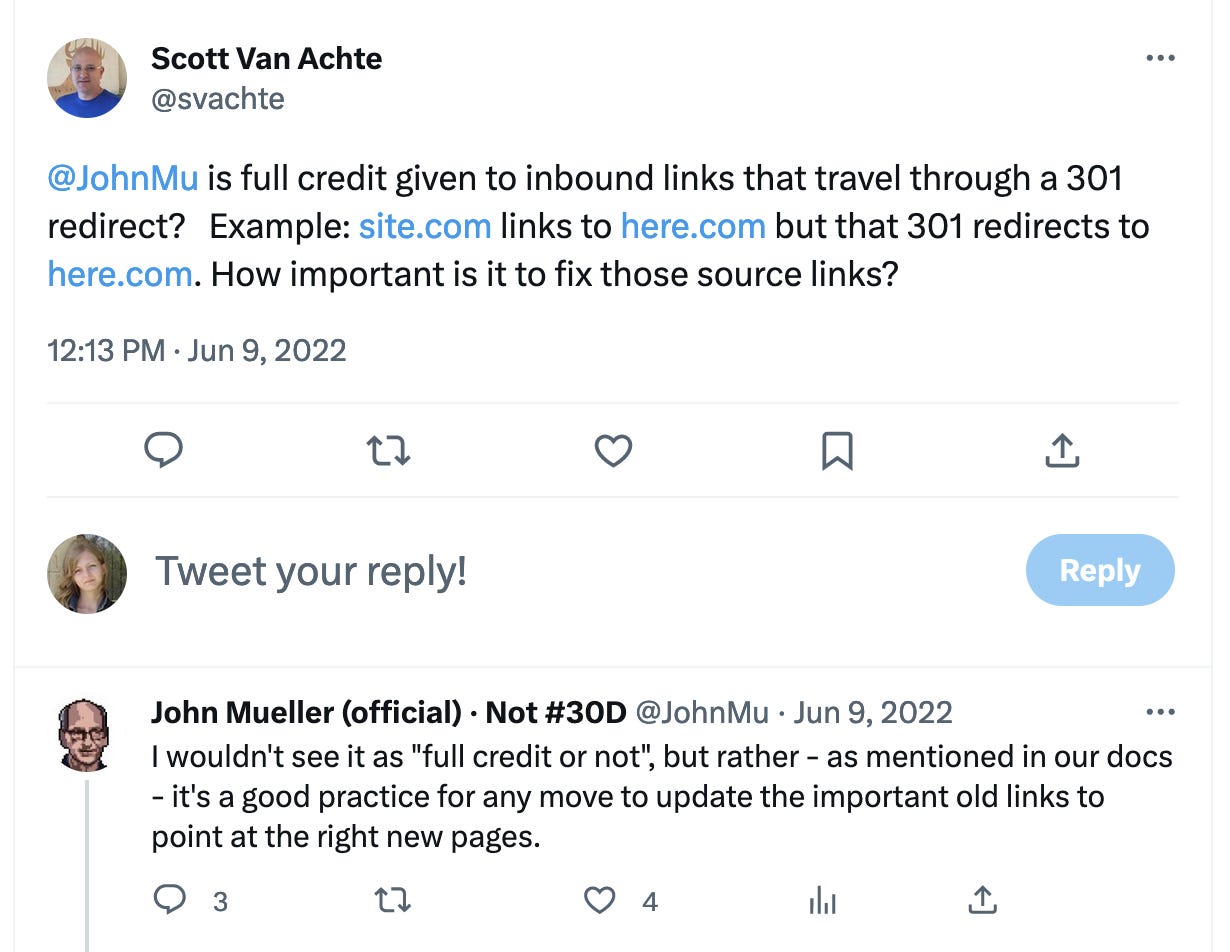
In 2022, John Mueller, Google’s Senior Search Analyst kind of confirmed that link equity can be lost through 301 redirects stating that you need to do your best to update old links in order to save more link equity:
Redirects Are Not to Be Used for URLs That Should Be 404s
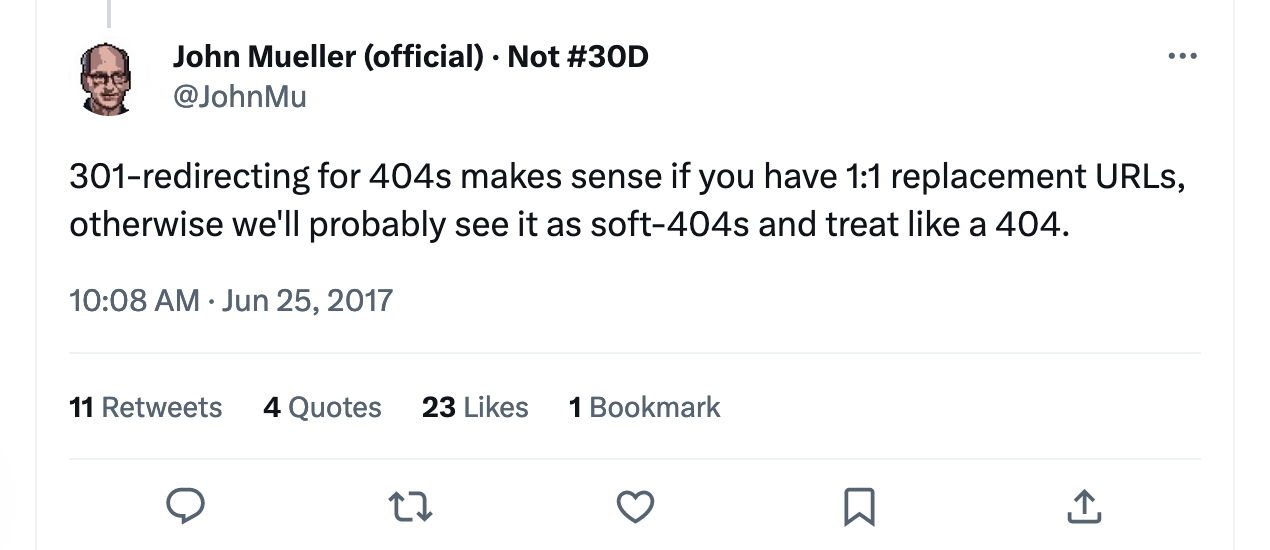
While passing link equity is always lucrative, Google states that redirects should only be used for 1:1 replacement URLs (for redesigns and site rebranding). If the redirected page is different than the original one, Google may treat it as a soft 404 and pass no link equity:
If your product has permanently expired, don’t redirect it to a new product (even if it’s a pretty similar product). In this case, let the expired product say “Sold out” and link to the new product. Yes, it is an extra step for your customers to make but it is better for usability (i.e. people not being confused about why they end up on a different product page) and SEO (at least some link equity will be passed through a link. Otherwise, Google may pass 0 treating the redirection as a soft 404).
301 Redirects: Best Practices
With all of those tests and clarifications in mind, here is how you really need to use 301 redirects:
If you can avoid changing URLs, try to avoid that. You will likely use organic traffic through redirects. Personally, I’ve never seen a URL 100% retain its positions after being redirected to a new destination
When changing the URL structure or rebranding to a new domain, make sure all the internal links are updated. If you link internally to a redirected page, you will lose some internal link equity and lose even more rankings.
If your product or page has expired, let it return a 404 response, even if it has some external backlinks. Google only passes link equity through redirects if it’s a 1:1 replacement (i.e. the new page is exactly the same).
As an extension from the previous point, if you need to update a page URL and its content, make sure to update the content prior to redirecting and let Google index it. Then, redirect it. This way Google will see a page being redirected to the exact same page and pass link equity through the redirect. Likewise, if it’s about changing a domain name, make sure Google indexes your redesigned site, then redirect it to your new domain. Make a thourough plan before even buying a domain name. Simply put, you need to make sure that Google sees these redirects as one page being redirected to its exact replacement, not a different page. This way changes to pass link equity are higher.
Likewise, if you are buying a site in order to make use of its link equity through a redirect, think twice. These redirects may or may not work, especially if the site is not exactly relevant to where you are about to redirect it.
In some cases, those redirects won’t be honored. In other cases, it may still cause a drop in rankings, if you fail to update internal (or even external) links. Sometimes, shortcuts work in SEO until they don’t! So make sure you plan your redirecting strategy carefully and implement additional changes (internal link changes and content updates) to be sure those redirects will work as intended.